Before proceeding with this mini-guide, it is assumed that you have already set up and have a functional Virtual Host. If you haven't done so, please consult the Virtual Host or Quick Start guides for detailed information.
By default, Mod Security is enabled in your web server configuration. While it can be disabled if absolutely necessary, it's generally recommended to keep it active.
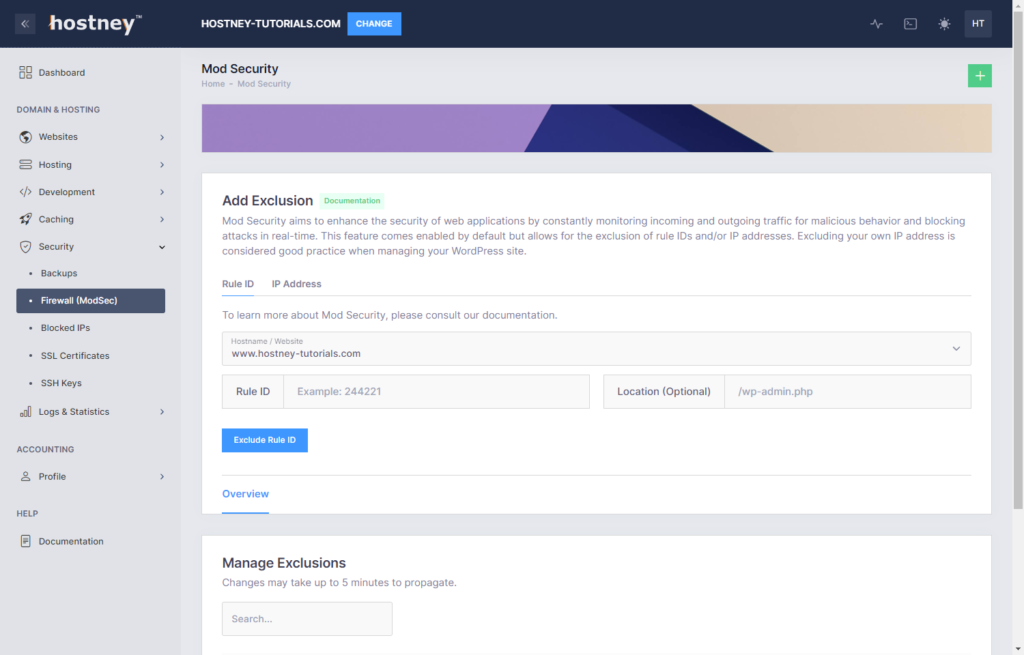
As a best practice, it's advised to regularly inspect your access and error logs to identify any Mod Security-related issues. If you come across specific Rule IDs causing problems, you can exclude them from the filtering process.
Additionally, if you encounter difficulties solely when managing your CMS (e.g., WordPress, Drupal), you can consider excluding your public IP address from Mod Security's filtering.
To perform these exclusions, navigate to the "Security" section, and select "Firewall (ModSec)." From there, find the appropriate tab, enter the Rule ID or IP Address you want to exclude, specify the location, and click the "Exclude" button to apply the changes.
Always exercise caution when adjusting security configurations to ensure the continued safety of your web applications.
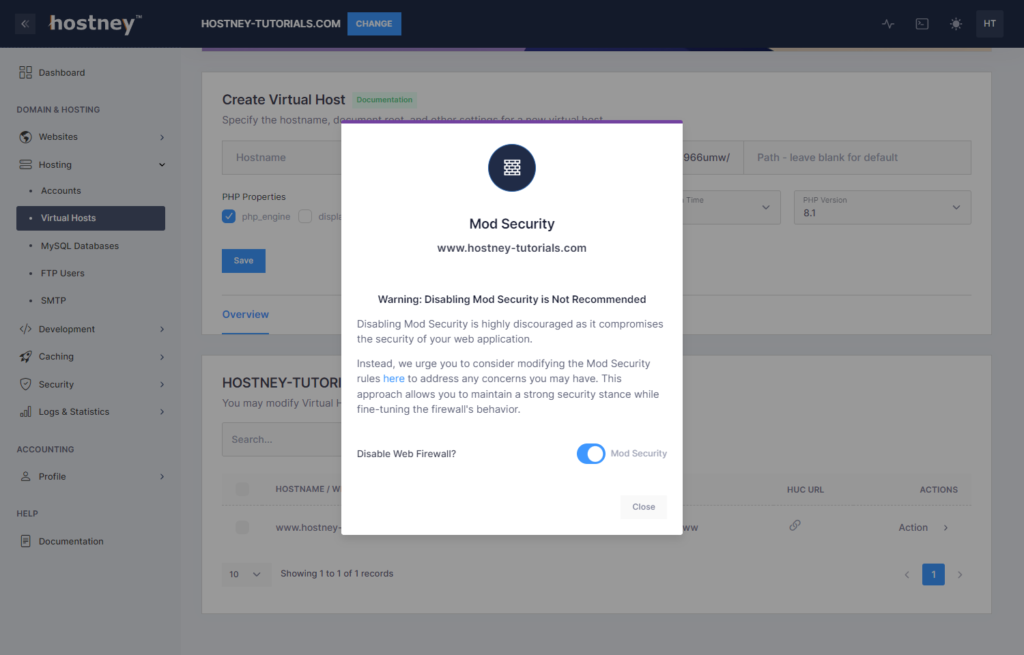
Warning: If you want to disable Mod Security, please note that this goes against best practices and may expose your website to security risks.
If you wish to disable Mod Security, the option is available for you to do so in the "Hosting" section of your control panel, specifically under "Virtual Hosts."
Locate your website in the list and then find the Mod Security option under the "Actions" menu. From there, you can choose to disable Mod Security as per your preference.